Stop Consonants
The stop consonants are characterized by a complete cessation and sudden release of airflow by the lips and/or the teeth and tongue at the start of the phoneme. The voiced stop consonants rely upon glottal impulses and vocal tract resonances; the unvoiced stop consonants are devoid of vocal tract activity and are dominated by fricative hiss. [2] A glottal stop is also included; this sound consists of a single click created by the sudden opening of the glottis.
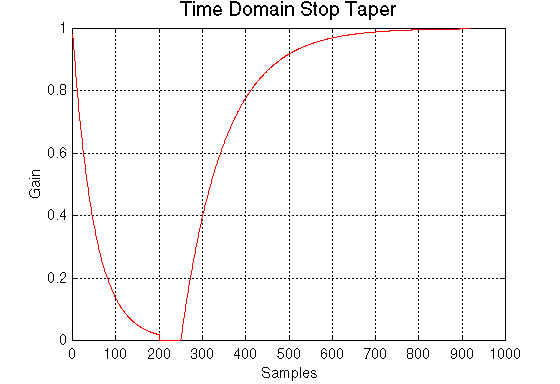
We modelled the stop consonants as we modelled other voiced or unvoiced phonemes. After creating the basic sound we applied an "ad hoc, non-criterion based" time domain envelope which ramps exponentially from zero amplitude to full amplitude. (Apologies are due to Dr. Don Johnson for the appropriation of his genteel phrase for "guessing.") We modelled the glottal stop with the application of a similar short time domain window with sharp edges to a filtered white process.
Timothy D. Dorney and Robert H. Sparr
Electrical and Computer Engineering Department, Rice University
April 1996