A Java program consists of one or more classes one of them must be public and must have a method with the following signature:
public static void main (String[] args).
Basically, the main method will instantiate appropriate objects and send them "messages" (by calling their methods) to perform the desired tasks.

// Line-oriented - comment goes to end of the current line.
/*
block-oriented
can span several lines.
*/
[…] means optional.
[public] class class-name [inheritance-specification] {
[field-list;]
[constructor-list;]
[method-list;]
}
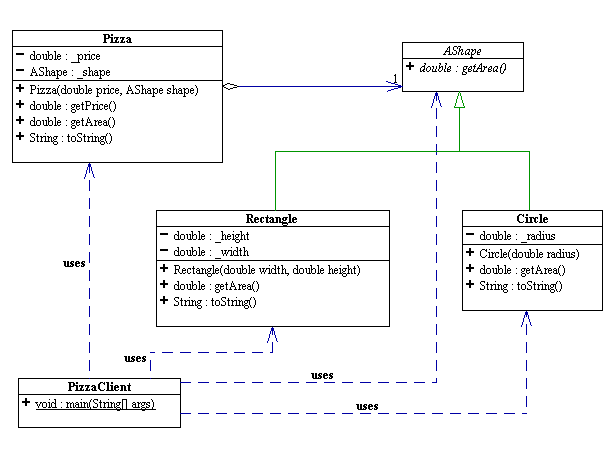
public class PizzaClient {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// instantiation and assignment.
Pizza cirPizz = new Pizza(4.69, new Circle(2.5));
Pizza rectPizza = new Pizza (4.49, new Rectangle (5, 4));
// output to standard output stream.
System.out.println(cirPizza); // cirPizza.toString() is called by default
System.out.println(rectPizza); // rectPizza.toString() is called by default
System.out.print("Round Pizza is a better deal than Rectangular Pizza: ");
System.out.println
((cirPizza.getPrice() / cirPizza.getArea() < rectPizza.getPrice() / rectPizza.getArea()));
// NOTE: infix notation for arithmetic expressions, and
// "dot" notation for method calls.
}
}
NOTE: Each Java statement must terminate with a semi-colon.
public class Rectangle extends AShape {
private double _height; // Note the underscore.
private double _width;
public Rectangle (double width, double height) {
_height = height;
_width = width;
// the underscore helps distinguish the field from the // parameter.
}
public double getArea() {
return _height * _width; // infix notation!
}
public String toString () {
return "Rectangle(width = " + _width + ", heigth = " + _height + ")";
}
}
Notes on the toString() method: toString() is a method that is inherited all the way from the base class, Object. It is the method that the Java system calls by default whenever a string representation of the class is needed. For instance, "This is "+ myObject is equivalent to "This is " + myObject.toString(). DrJava will call an object's toString() method if you type the object's name in the interaction window, without terminating the line with a semicolon. The return value of toString() is what prints out on the next line.
A field list consists of zero or more field declarations of the form
[static] [final] [public | private | protected] field-type field-name [assignment];
A constructor list consists of zero or more constructor definitions of the form
[public | private | protected]
class-name ([parameter-list]){
[statement-list;]
}
NOTE: The constructor's name is the same as the class name. Constructors are used for initialization of the object during the object's instantiation only.
A method list consists of zero or more method definitions of the form
[static] [final] [public | private | protected]
return-type method-name [param-list] {
[statement-list;]
}
A return type void means the method does not return any value.
param-list looks like:
type1 param1, type2 param2, …, typeN paramN