COMP 310
Fall 2012
|
Lec25: Remote
Method Invocation (RMI)
|

 |
Today we will start exploring the world of Remote Method Invocation or "RMI".
The demo code for today can be obtained by creating a
new project in Eclipse and setting the
svn:externals property for the "src"
folder to
"provided https://svn.rice.edu/r/comp310/course/RMIHelloWorld/provided".
The demo code consists of two executable classes, a "client" and a "server"
plus an interface that defines the remote service that the server offers to the
client.
Be sure that the
Server machine has the Server.REGISTRY_PORT
and Server.SERVER_PORT open through its
firewall!!
To run the server:
- Highlight the Server file and click
Run.
- The Server must be started first,
otherwise the Client will have nothing to
connect to.
- You should see a "Server ready" message
on the console if the Server has started
succesfully.
- Highlight the Client file and click
Run.
- The client should instantiate, connect to the
Server, print the response from the Server
and exit.
- To connect to a remote machine, edit the launch configuration for
the Client and put the IP address for the
remote server as a "Program Argument".
See the Eclipse Resources web page on
Editing the Launch
Configuration Parameters.
To stop the running server:
- Change to the server's console by either closing the console of the
client if it open by clicking the "x" on the console tab or by selecting the
server's console by pulling down the "Display Selected Console" drop-list on
the console tab.
- Click the red square "Terminate" button on the console tab.
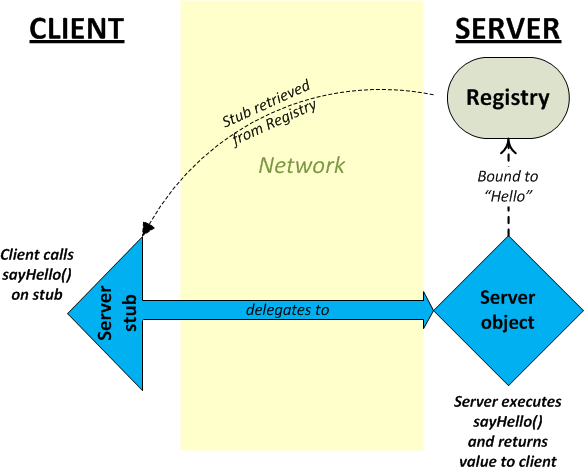
What's going on:
-
The server binds a Server
stub (a Hello interface implementation just like
Server itself) to the name "Hello"
in the Registry.
-
The client asks for the name "Hello"
in the server's Registry and receives the stub to the
Server object.
-
The client calls sayHello()
on the stub object.
-
The stub transparently delegates the call all the way
across the network to the actual Server object
on the server machine.
-
The Server object runs
its sayHello() method and returns the result.
-
The stub returns the result across the network back
to the waiting client.
Things to try:
To create your own modifications, simply create
your own Client, Server,
and Hello classes in your
own package by copying the code from the provided
package and then adjusting the package references.
Do NOT edit the code in the
provided package as you will not be able to commit your code!
- Bind multiple Server implementations to the
same name in the Registry:
- Start the original Server.
- Change the return value of sayHello()
method of the Server class to return a
different value.
- Change the port value that the server object is being bound to from
SERVER_PORT to
SERVER_PORT+1 (Otherwise you might get a port conflict error)
- Without terminating the previous
Server , run the Server again.
- Without modifying it, run the Client
again.
- Even though the original Server is
still running, what is the value retrieved by the
Client?
- Bind multiple Server implemenations to
different names in the Registry.
- Start a version of the Server.
- Run the Client to verify the value
returned is what you expect.
- Modify the Server's
sayHello() method to return a different
value.
- The new Server should bind the server
object should change the port value that the server object is being
bound to to a different port than the original
Server e.g. SERVER_PORT+1
(Otherwise you might get a port conflict error)
- Modify the Server's
run() method to bind the
Hello object with a different name.
- Without terminating the previous
Server , run the Server again.
- Without modifying it, run the Client
again. What value is returned?
- Modify the Client so that it accesses
the new Registry binding name being used in the modified
Server code above.
- Run the Client again.
What value is returned?
© 2012 by Stephen Wong
