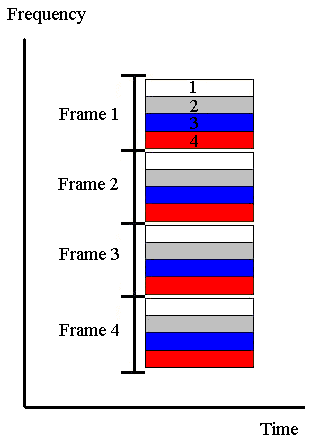
Frequency Division Multiple Access
The successful wireless
transmission of data depends upon three major factors: fairness, efficiency,
and data collision avoidance. Frequency Division Multiple Access (FDMA) accomplishes
this goal by equally dividing its frequency spectrum among users. After the
division of the frequency spectrum into frames, the protocol allocates one section
of each frame (frequency slots) in which one user may transmit. Thus, a user
may transmit over all time while remaining limited to a certain frequency bandwidth.
FDMA successfully accomplishes only two of the three major objectives that it
sets out to achieve. An idle user in the system wastes its bandwidth since FDMA
has no ability to redistribute the resources among the other active users.
