Time Division Multiple Access
In order to successfully
transmit data, a protocol must be developed ensuring fairness, efficiency, and
a lack of data packet collisions. One such method is Time Division Multiple
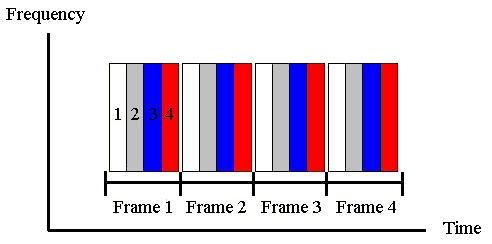
Access (TDMA). This method evenly divides time between certain numbers of users,
thus guaranteeing each user a certain amount of network resources. Time is separated
into finite length frames, with each frame being partitioned into slots. Each
user on the network is designated one of these slots. Consequently, the user
may transmit only during this time period (slot) over all frequencies, and then
must wait until its next transmission slot in the following frame. This technique
succeeds in two major areas. First, it evenly divides the available resources
(time) among the number of users on the network. Second, it guarantees freedom
of data packet collisions by ensuring that only one user transmits at a time.
However, TDMA suffers one significant drawback. Idle users waste network resources
because their time slots cannot be redistributed to other needy users.
