| The Playing Card Image Recognition Project by SethE Ben Graf Michael Victory Ray Wagner |
||||||
FINAL REPORT Introduction Introduction Initial Experimentation Initial Experimentation Card Detection Process Overview Card Detection Process Overview Rotation Rotation Results Results MATLAB Code MATLAB Code Demos Demos Division of Labor Division of Labor Acknowledgements Acknowledgements Consulted Sources Consulted Sources |
||||||
|
Introduction Image recognition is a hot research topic these days. Many industries have welcomed the new technological developments from this field. Pharmaceutical companies can scan an packing line to verify that every package contains the correct number of pills. Microchip makers possess the ability of early detection of errors in manufacturing to cut down production costs. The goal of this project is to develop an image recognition system for another market: casinos. An offbeat but useful application for this market is recognition of images of playing cards. In a casino setting, this recognition system would allow constant watch over the state of card games. Such vigilance could allow for the elimination of unscrupulous players and inept dealers. This project, coded entirely in MATLAB, sets out to demonstrate how such an image recognition system could be implemented. Given an image from a ceiling or table camera, this system would be able to identify the value and suit of all cards in the image. Initial Experimentation In the early development of this project, correlation of playing cards was the primary concern. From past assignments, the matched filter, based on the Cauchy-Schwarz theorem, performed well. This filter was implemented in coc.m to verify that the filter would function in the project. In correlating the FourClubs with the TwoClubs, itself and the SixClubs, the following correlations resulted:
Correlating the Fourier transform representations of playing card images was also experimented with to find a potentially stronger correlation scheme. The two dimensional Fourier transform representation were taken of the three previous cards and were correlated with the matched filter. The process was implemented in ffcoc.m Here are the TwoClubs and FourClubs and their respective 2d Fourier transforms:
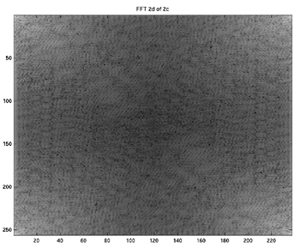 2D FFT of TwoClubs  2D FFT of FourClubs
 Next: Page 2 Next: Page 2 |
||||||